Tagify™ i5 UMI Adapter-loaded Transposase
Tagify™ i5 UMI Adapter-loaded Transposase enables simple, scalable, and reliable NGS library preparation that requires unique molecular identifier (UMI) addition.
- Supports GUIDE-seq2 off-target analysis and other UMI-based assays
- Quickly and reliably fragment and tag genomic DNA via loaded Tn5 transposase
- Sequence tag includes Illumina-compatible i5 barcode and UMIs
- Fully QC’d reagent for reproducible tagmentation
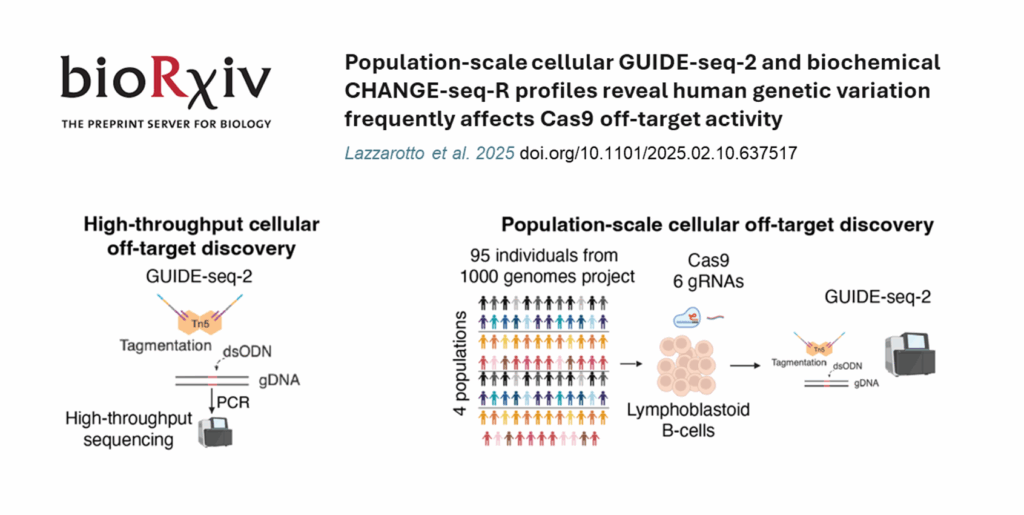
Tagify UMI in Action: GUIDE-seq2
GUIDE-seq2 , the second generation of GUIDE-seq, delivers a more sensitive, reproducible and scalable assay by integrating tagmentation into the library preparation workflow, while retaining the assay’s proven biology. Tagify i5 UMI is a commercial source of fully QC-ed, ready-to-use loaded transposase that unleashes the power of GUIDE-seq2!
Tagify i5 UMI Adapter-loaded Transposase
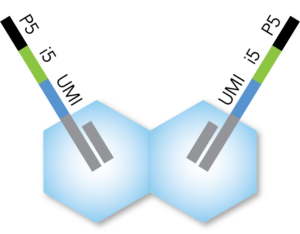
- Each transposase is loaded with a full-length Illumina-compatible P5 + i5 + UMI + R1 adapter
- 10-bp i5 barcode and 10-bp UMI
- Available in sets of 24 unique i5 loaded transposases. Additional indexes available upon request.
![]()
How Can Tagify UMI’s Help You?
“We use seqWell’s custom Tagify reagent for our UDiTaS process. The batches are consistent and provide similar tagmentation profiles and editing results. The reactions can be scaled from 96 to 384 wells, and we’ve been able to process thousands of reactions over one year.”
– Georgia Giannoukos, Ph.D., Director of Next Generation Sequencing, Editas Medicine

Recorded Webinar
Assessing CRISPR On-Target Editing and Structural Changes
In this webinar, Dr. Giannoukos highlighted how her team combined a custom Tagify reagent with their UDiTaS method to measure large deletions and inversions at the CEP290 editing site.
She also incorporated data demonstrating reproducibility of different Tagify batches. This webinar was transcribed into a blog if you prefer to read along.
Looking for a transposases loaded with a different payload?
Check out our Tagify Custom-loaded Transposase Reagents
Tagify i5 UMI Reagent Specifications
| Specs | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Applications | CRISPR or Gene Editing QC and Verification |
| Sample Types | Genomic DNA |
| Reactions per Kit |
|
| Standard dispense volume per well | 3μl or 4μl in a 96-well microtiter plate |
| Transposase | Hyperactive Tn5 |
| DNA Input Recommended | 50ng |
| Number of unique barcodes | 24 i5 indexes with unique molecular identifiers(UMI). Inquire for additional i5 indexes at sales@seqwell.com |
| Barcoding Strategy |
|
| Standard Output Fragment Range** (measured with Agilent DNA BioAnalyzer Chip) | 800 – 2000 bp (using region mode with a range of 200 – 7500 bp) |
| Sequencer Compatibility | All Illumina sequencing platforms; Use with Element Biosciences AVITI™ or other sequencing platforms is possible with conversion kits for Illumina libraries |
**Because the tagged product in not a complete NGS library, sizing data and traces obtained from other methods, such as Agilent TapeStation or Femto Pulse, may vary.
Applications* – commercial use may require a license from a third party.
1. UDiTaS Method: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5861650/
3. RGEN-Seq Method: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34880355/