Featured Publications
Explore peer-reviewed journals and other accredited publications that highlight how seqWell technology is revolutionizing next generation sequencing.
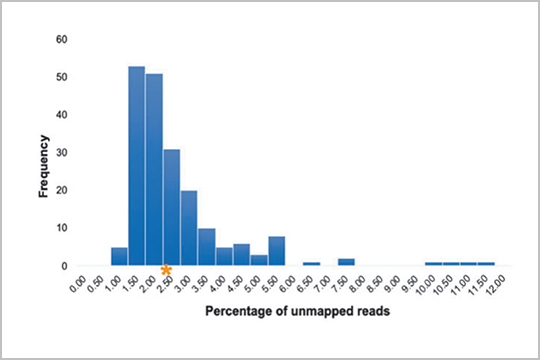
APPLICATION: Plasmid Sequencing
Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) vectors are growing increasingly popular as gene delivery tools within biological systems. In “A Novel Next-Generation Sequencing and Analysis Platform to Assess the Identity of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viral Preparations from Viral DNA Extracts”, Guerin et. al provide a detailed protocol for simple and rapid NGS of rAAV genomes from DNA extracts.
The study authors used our plexWell 96 kit to generate libraries of purified vector DNA post AAV production. Sequencing was used to assess the amount of contamination in production from the originally designed vector, which was also sequenced with seqWell technology.
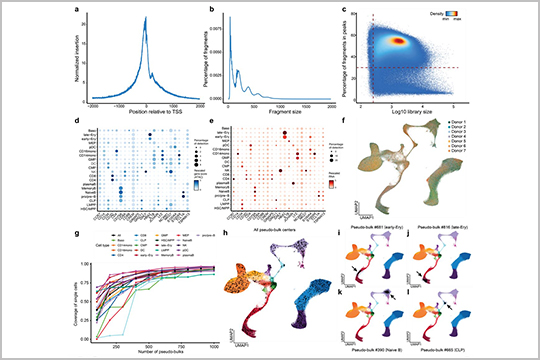
APPLICATION: SHARE-seq
This publication discusses the importance of cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) in regulating gene expression, and how their structural changes can affect cell function and development. Hu et al. introduce a new computational approach called PRINT (Protein-Regulatory element Interactions at Nucleotide resolution using Transposition) that corrects for sequence bias and allows for multi-scale footprinting, which can accurately predict TF binding at cCREs.
The authors used seqWell’s Tagify™ enzyme to perform the SHARE-seq assays that underlie the data used for this new method.
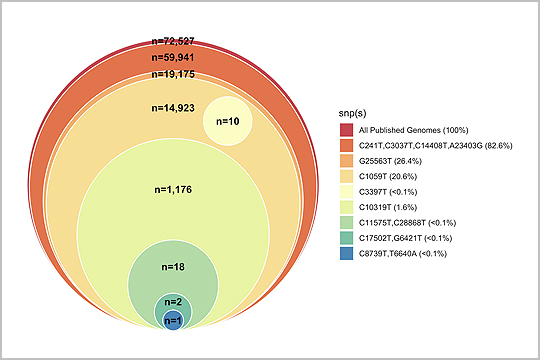
APPLICATION: Amplicon Sequencing
In this 2022 publication, titled “Sequencing the pandemic: rapid and high-throughput processing and analysis of COVID-19 clinical samples for 21st century public health”, Folkerts et al. used our plexWell™ 384 kit to generate libraries from SARS-CoV2 amplicons generated from the ARTIC protocol.
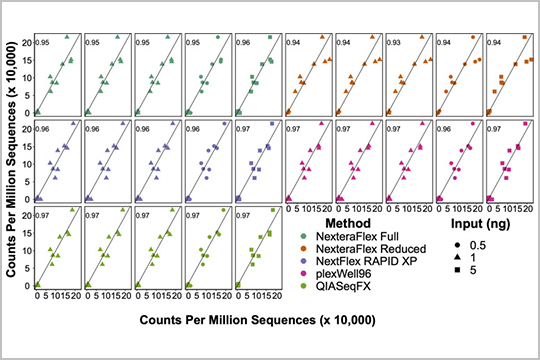
APPLICATION: Metagenomics
Gaulke et al. evaluated our plexWell 96 library prep kit against four other kits for microbial metagenomics sequencing of water, coral, fecal, and soil samples in their study “Evaluation of the Effects of Library Preparation Procedure and Sample Characteristics on the Accuracy of Metagenomic Profiles”.
The authors reported that plexWell 96 was one of the most economical choices for metagenomic library generation.
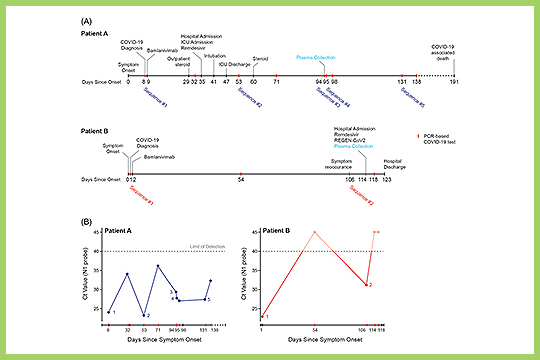
APPLICATION: Whole Genome Sequencing
Simons et al. used our plexWell 384 kit in their study “De novo emergence of SARS‐CoV‐2 spike mutations in immunosuppressed patients”.
The authors sought to assess the emergence and frequency of spike mutations in immunocompromised patients and hypothesized that such mutations might arise in the context of persistent viral replication in immunosuppressed hosts.
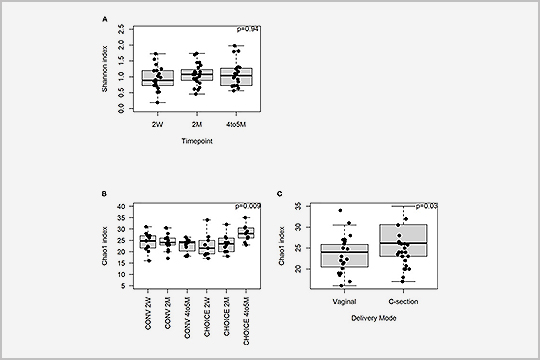
APPLICATION: Metagenomics
In “A maternal higher-complex carbohydrate diet increases bifidobacteria and alters early life acquisition of the infant microbiome in women with gestational diabetes mellitus”, published in July 2022, researchers used metagenomics to better understand the maternal and infant microbiome in women with gestational diabetes mellitus.
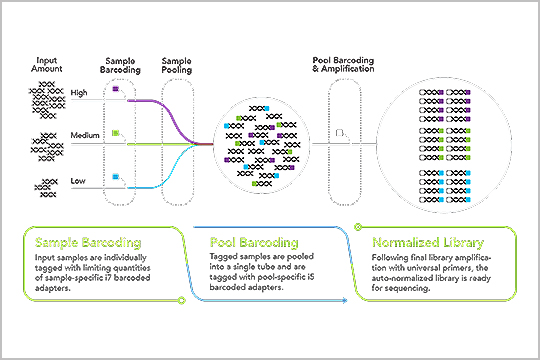
APPLICATION: Low-pass Whole Genome Sequencing
“The plexWell LP384 library prep method provides the dramatically increased throughput and reduced costs required to replace array for extremely large studies,” Peng Zhang, Hua Ling, Justin Paschall, Beth Marosy, Jessica Gearhart & Kimberly Doheny from the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR), Department of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, stated in a posted they presented at AGBT General Meeting this year in Orlando, FL.
Read the poster, “Evaluation of low-pass whole genome sequencing as a cost-effective alternative to array-based imputation”, and learn how the plexWell LP384 prep workflow saves time and cost.
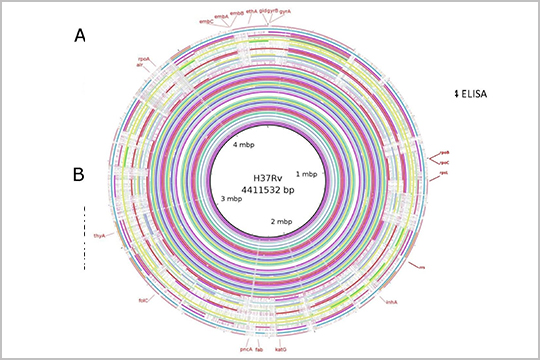
APPLICATION: Bacterial Whole Genome Sequencing
“Snapshot of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Phylogenetics from an Indian State of Arunachal Pradesh Bordering China” uses whole genome sequencing to correlate multiple strains of tuberculosis in the region. Genomic DNA was prepared for sequencing using the plexWell WGS-24 Library Preparation Kit.
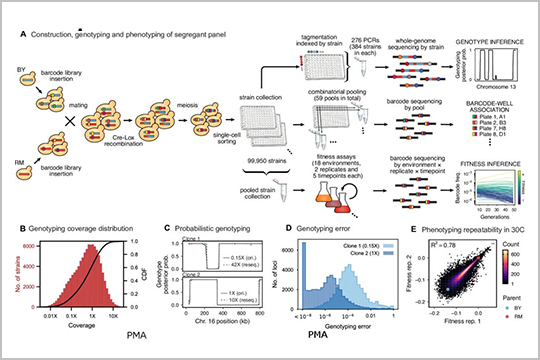
APPLICATION: CRISPR/Cas9 QC
This 2022 publication, “Barcoded bulk QTL mapping reveals highly polygenic and epistatic architecture of complex traits in yeast”, explores barcoding bulk quantitative trait locus mapping. The paper discusses strategies to increase the scale of the study by use of combinatorial index strategies, minimization of pipetting and purification steps, and use of seqWell’s transposase-based reagents that incorporate index adapters directly into the samples.
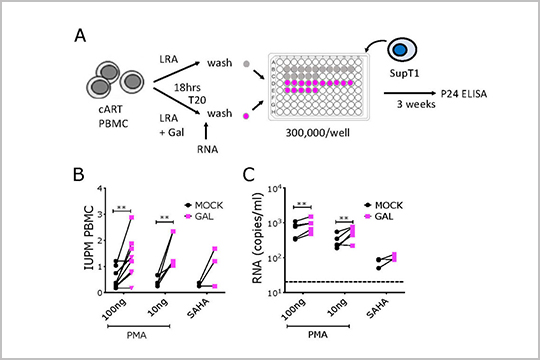
APPLICATION: Amplicon Sequencing (Viral)
In this publication by Samer, et al., “Blockade of TGF-β signaling reactivates HIV-1/SIV reservoirs and immune responses in vivo”, our plexWell 384 kit was used to prepare library from gag gene amplicons.
The plexWell 384 kit contains four assay-ready, 96-well PCR plates that are fully-skirted and low-profile and offers barcode combinations to multiplex up to 2,304 samples in a single lane.
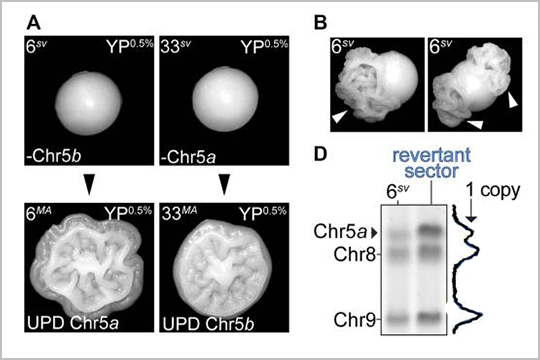
APPLICATION: Whole Genome Sequencing
Our plexWell-96 kit was used to pool and barcode libraries of individual genomes in this March 2022 publication, “Bursts of genomic instability potentiate phenotypic and genomic diversification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.”
This research article uses whole genome sequencing to understand the mechanistic basis of colony morphology phenotype switching which occurs in populations of a pathogenic isolate of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The results demonstrate that the colony morphology switching behavior is driven by evolution of the genome.
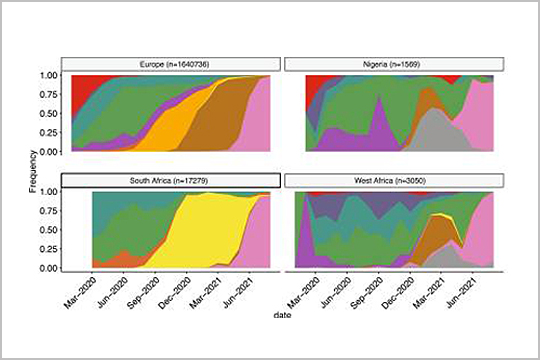
APPLICATION: SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing
Our plexWell 384 kits were used in sequencing library preparation of genome amplicon pools in this 2022 publication, “Multiple expansions of globally uncommon SARS-CoV-2 lineages in Nigeria”.
Read the full publication to find out how, as the authors wrote, “these results underline the critical importance of improving genomic surveillance efforts to better understand and monitor new variants as they arise in distinct regions of the globe.”
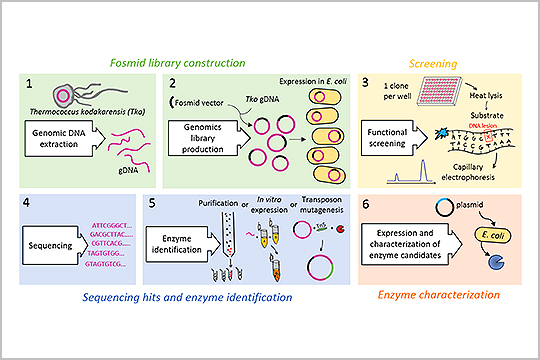
APPLICATION: High-throughput Screening
New England Biolabs multiplexed sequencing libraries using our plexWell 384 Library Preparation kit in the study, “Capillary Electrophoresis-Based Functional Genomics Screening to Discover Novel Archaeal DNA Modifying Enzymes”.
The authors reported that plexWell 384 provided “a rapid, simple, high-throughput method to discover novel archaeal nucleic acid modifying enzymes by utilizing a fosmid genomic library, next-generation sequencing, and capillary electrophoresis.”
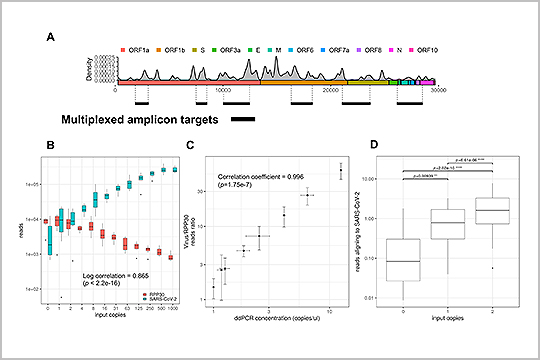
APPLICATION: SARS-CoV-2 Sequencing
The SARS-CoV-2 genome is susceptible to mutations during viral replication due to the errors generated by RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. In “Profiling SARS-CoV-2 mutation fingerprints that range from the viral pangenome to individual infection quasispecies”, Lau et. al identified quasispecies mutations occurring within individual patients, mutations demarcating dominant species, and the prevalence of mutation signatures. Analysis of these genetic fingerprints may provide a way of conducting molecular contact tracing.
The study authors used our plexWell 384 kit to generate libraries of a mix of 6 amplicons per SARS-CoV2 sample ranging from 1-2.67kb, designed to target all the known diversity of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Talk to our sales team about your research project.
We offer cutting-edge library prep technology suitable for a variety of applications. Contact sales to discover which product is right for your research.
